Pathogenesis Of Gaucher Disease
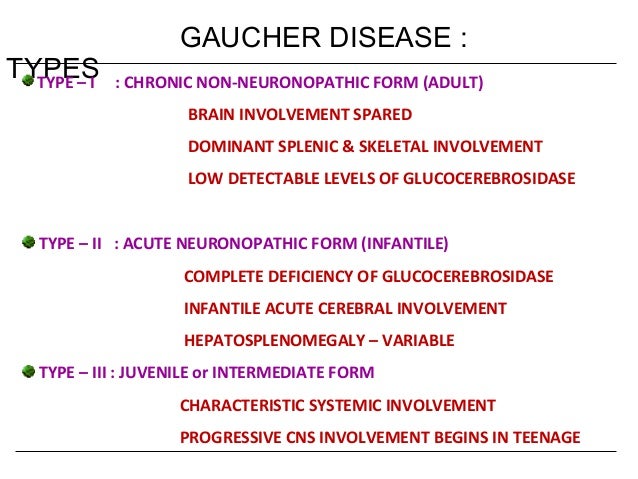
Pathogenesis of gaucher disease. Gaucher disease is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the gene. Clinical spectrum and types of Gaucher disease. Gaucher disease GD is an inborn error of metabolism that affects the recycling of cellular glycolipids.
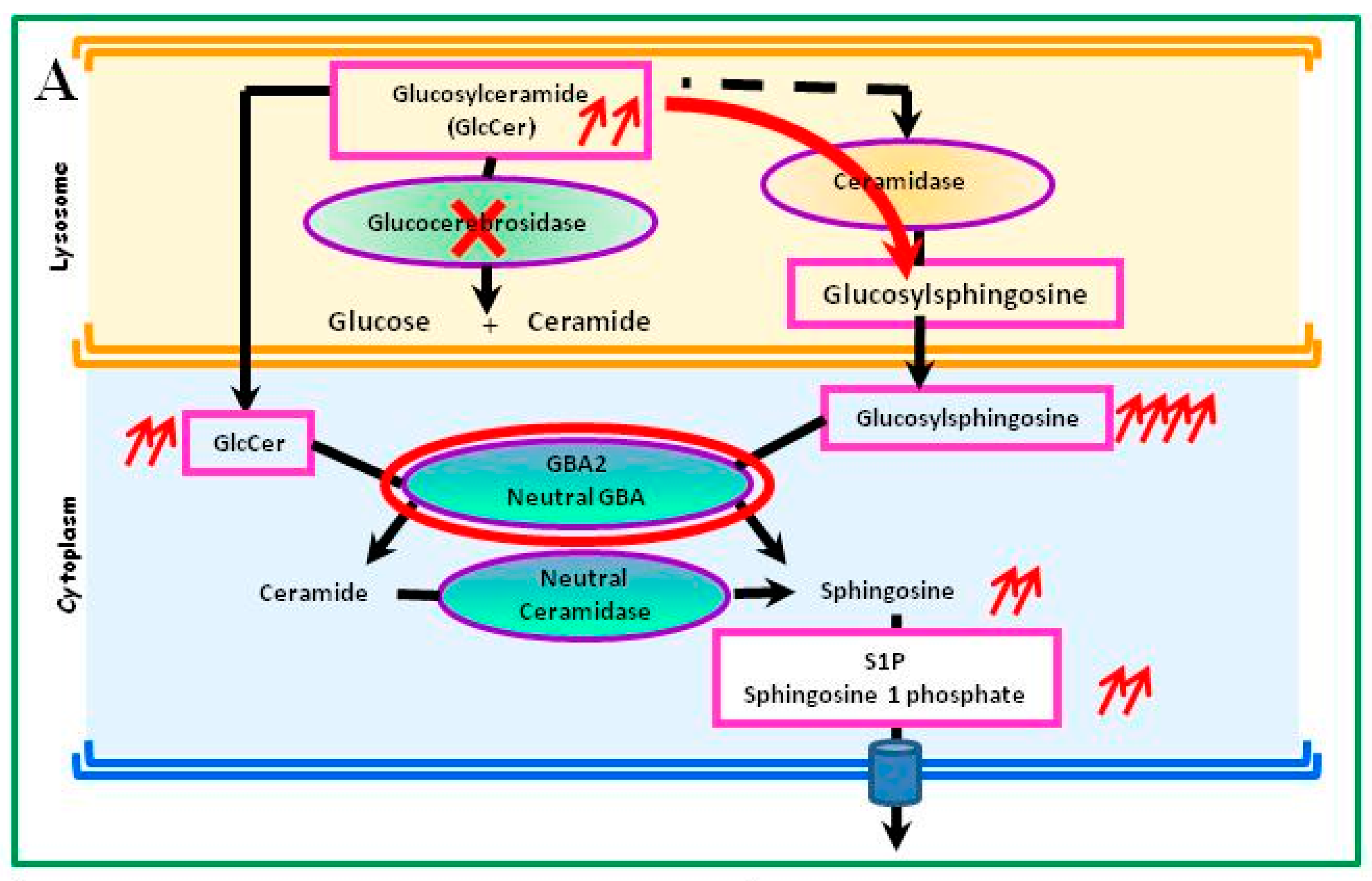
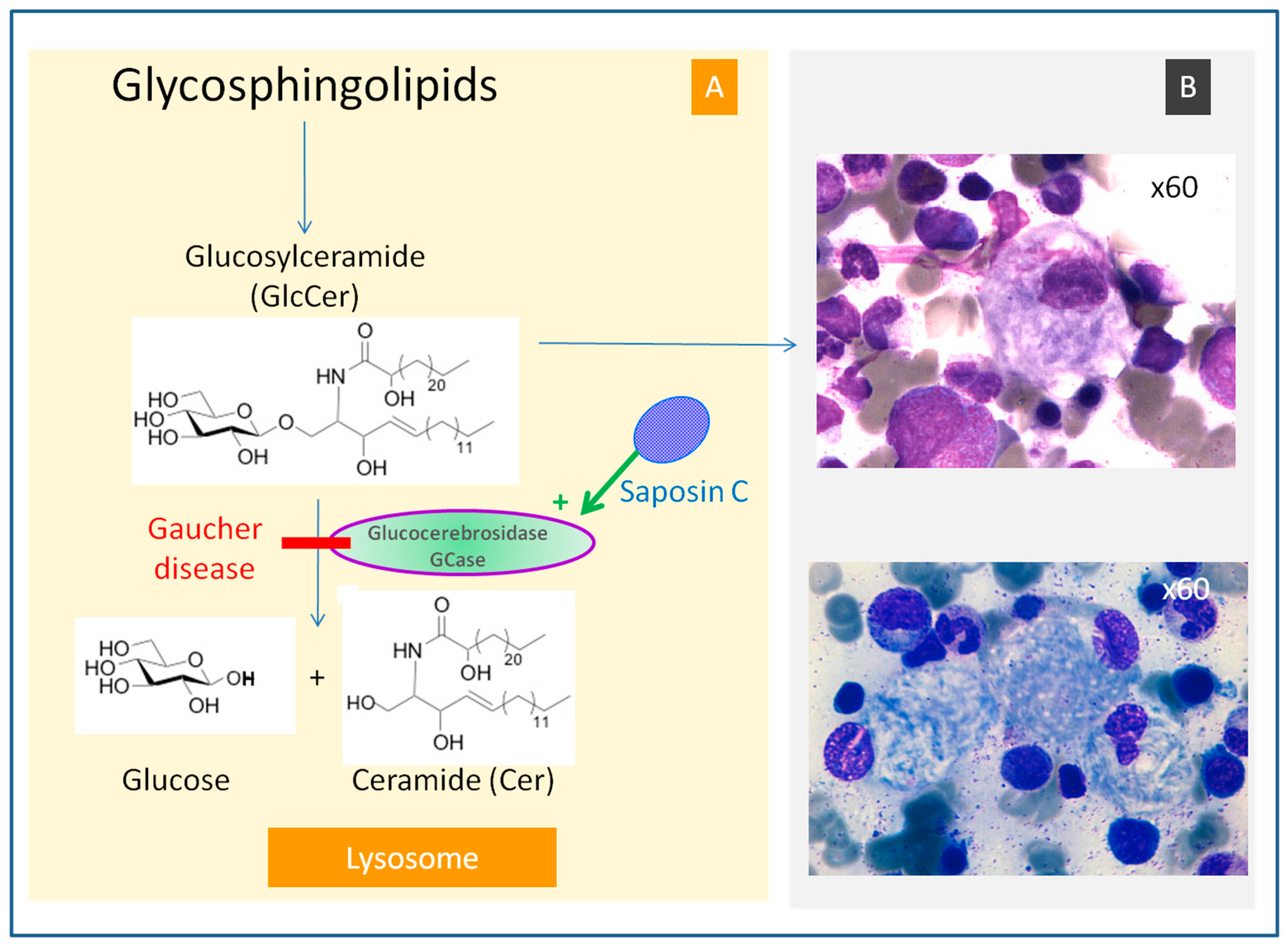
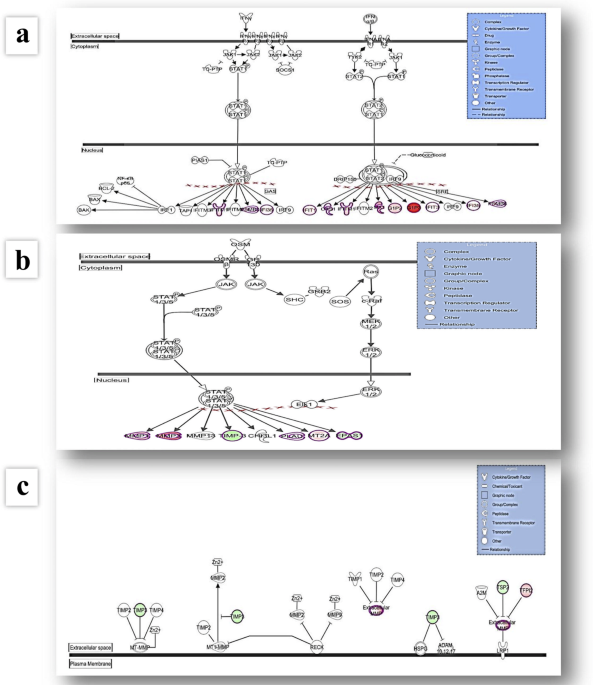
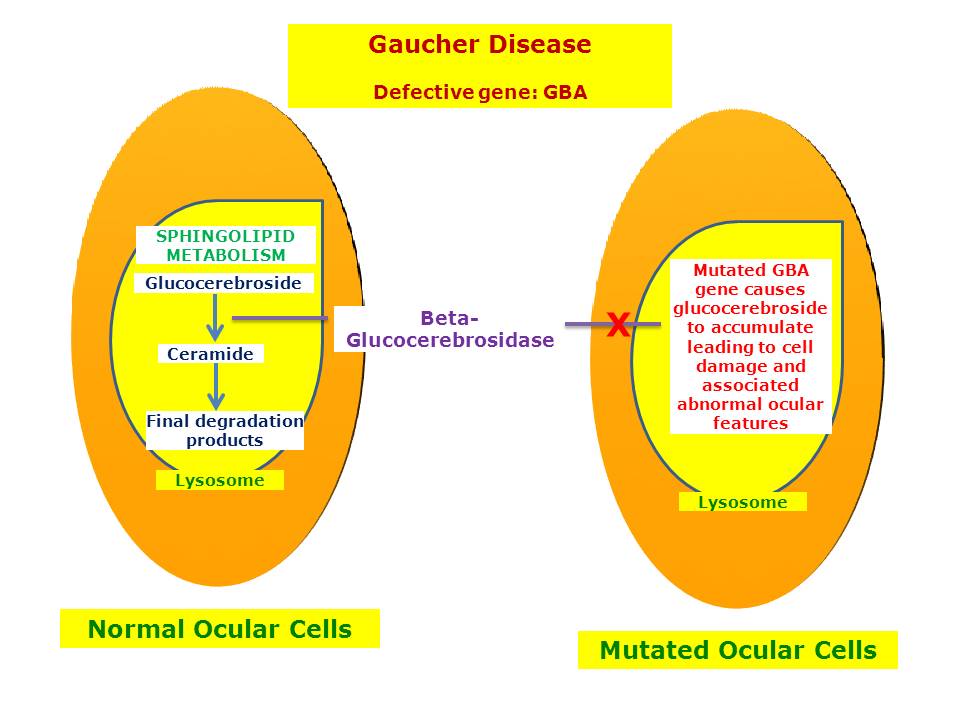
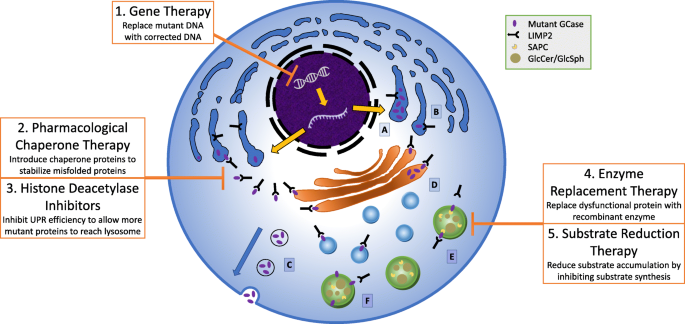
Gaucher disease is caused by mutations in the Gba1 gene encoding an acid β-glucocerebrosidase GBA1 the lysosomal hydrolase which breaks down glucosylceramide GlcCer. The Role of Immune System 1. Gaucher disease is a typical lysosomal storage disease resulting from an inborn deficiency of glucocerebrosidase.
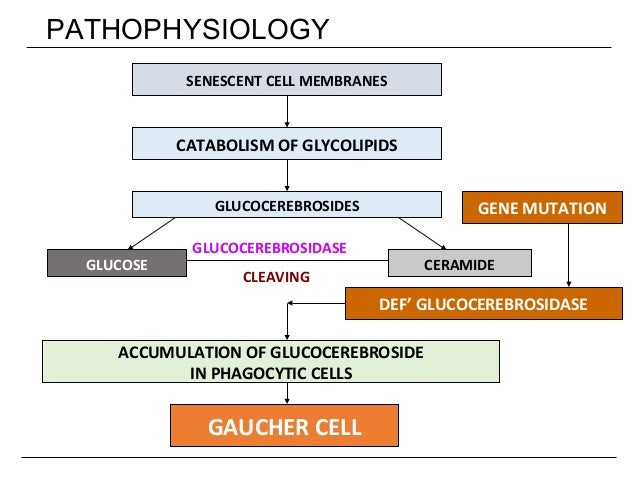
Gaucher the most prevalent lysosomal disorder is an autosomal recessive inherited disorder due to a deficiency of glucocerebrosidase. Glucocerebroside also called glucosylceramide and several related compounds that are ordinarily. It is caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase which leads to an accumulation of its substrate glucosylceramide in macrophages.
To investigate the possible role of cytokines in the systemic and local manifestations of established Gauchers disease. In addition disease of the nervous system can arise as a result of the accumulation of endogenous. Osteoimmunology in Pathological Conditions.
What is Gaucher disease. A diverse number of interactions between bone and immune cells occur within the bone. Glucocerebroside also called glucosylceramide and se.
This leads to the accumulation of glycolipidsin macrophages particularly those in the liver bone marrow spleen and lung. In Gaucher type 1 disease the accumulation of this simple glycolipid is mainly restricted to tissue phagocyte lysosomes resulting ultimately in hepatomegaly splenomegaly and. Gaucher disease has recently been questioned 8 Gaucher skin fibroblasts are not important in Gaucher disease.
This leads to the accumulation of glycolipids in macrophages particularly those in the liver bone marrow spleen and lung. Gaucher disease is caused by mutations in the Gba1 gene encoding an acid β-glucocerebrosidase GBA1 the lysosomal hydrolase which breaks down glucosylceramide GlcCer.
A diverse number of interactions between bone and immune cells occur within the bone.
Gaucher disease is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the gene. The activation of immune cells is a requisite for defense of the. In the general population its incidence is approximately 140000 to 160000 births rising to 1800 in. Gaucher disease is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the gene. It is caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase which leads to an accumulation of its substrate glucosylceramide in macrophages. Gaucher disease GD is an inborn error of metabolism that affects the recycling of cellular glycolipids. Glucocerebroside also called glucosylceramide and several related compounds that are ordinarily. Glucocerebrosidase deficiency leads to the accumulation of glucosylceramide primarily in cells of mononuclear-macrophage lineage. To investigate the possible role of cytokines in the systemic and local manifestations of established Gauchers disease.
The activation of immune cells is a requisite for defense of the. GCase deficiency results in progressive intralysosomal accumulation of glucosylceramide in different tissues primarily in cells of mononuclear-macrophage lineage. Gaucher disease GD ORPHA355 is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder. The Role of Immune System 1. Gaucher disease has recently been questioned 8 Gaucher skin fibroblasts are not important in Gaucher disease. The molecular diagnosis of Gaucher disease has been difficult due to the existence of several different point mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene and due to the presence of a tightly linked highly homologous pseudogene. This leads to the accumulation of glycolipids in macrophages particularly those in the liver bone marrow spleen and lung.




































Post a Comment for "Pathogenesis Of Gaucher Disease"